Global Environmental Conservation
We work for environmental conservation in order to reduce the impact of our business operations, products and service on environment, and make continuous improvements.
Fundamental Environmental Policy and Mid- to Long-term Environmental Plans
Fundamental Environmental Policy
In recent years, we understand that our stakeholders have become increasingly concerned about our environmental issues, including climate-related issues. In such a situation, we believe that we are socially responsible for realizing a low-carbon society and contributing to a recycling-oriented society.
The GS Yuasa Group has established this Fundamental Environmental Policy to outline our basic Group-wide approach to environmental efforts. The policy aims to clarify our social responsibility toward the environment and guide our contributions to the emergence of a sustainable society. We are also developing and using environmental management systems that will help to reduce environmental impacts and prevent any accidents that could cause environmental pollution.
Fundamental Environmental Policy
-
Fundamental Philosophy
We are committed to people, society, and the global environment through the “Innovation and Growth” of our employees and business entities. We will apply the advanced energy technologies we have built up through battery research and development work to deliver comfort and peace of mind to customers around the world, and aim to realize a sustainable society and increase corporate value.
-
Action Guidelines
- Compliance with laws, regulations, and other requirements
We will strive to prevent environmental incidents, comply with legal requirements, and reduce risks connected with the use of chemical substances, and continually improve our environmental management system with the aim of enhancing our environmental performance.
- Reducing environmental burden
We will aim to be carbon neutral by reducing greenhouse gas emissions throughout our supply chain to limit climate change impacts. We will also recognize water as an important resource and strive to conserve it by reducing consumption levels.
- Efficient utilization of natural resources
Toward a circular economy*, we will strive to minimize the amount of natural resources we use through a range of means, including reducing raw material usage, using recycled materials, and reducing waste throughout product life cycles and services.
- Environment-friendly products
To be able continue “creating the future of energy”, we will develop and manufacture products and services that can contribute to the formation of a carbon-neutral circular economy.
- Biodiversity
Given that our business activities, products, and services depend on the natural environment, we will promote biodiversity conservation activities to protect the ecosystems of endangered and rare species.
- Disclosure
We will disclose environment-related information to stakeholders in an appropriate manner, and strive to coexist harmoniously with communities by engaging in proactive communication.
- Human resources development
We will foster, across the entire GS Yuasa Group, personnel able to forge the future of our business with the aim of meeting our responsibilities in helping to create a carbon-neutral circular economy.
Resource recycling society with zero waste
- Compliance with laws, regulations, and other requirements
Mid- to Long-term Environmental Plans
We have developed mid-term plans for important issues related to our fundamental environmental policy in order to contribute to the emergence of a sustainable society. Since fiscal 2019 we have been promoting this as one of our business strategies to address key management issues that concern the entire Group by incorporating environmental objectives into our Mid-term Management Plan.
In April 2023, the GS Yuasa Group announced our Carbon Neutrality Declaration in the pursuit of reaching zero CO2 emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2) from our business activities by fiscal 2050. As specific milestones for achieving our Carbon Neutrality Declaration, we have set CO2 emission reduction targets through fiscal 2030 and CO2 emission reduction targets in our Mid-term Management Plan. Going forward, the Group will continue to actively promote initiatives to mitigate climate change (energy conservation activities, use of renewable energy, etc.) with the aim of achieving carbon neutrality.
Mid- to Long-term environmental goals
Please scroll sideways
| Items | Medium-term goals (FY 2025) |
Long-term goals (FY 2030) |
Results (FY 2024) |
Results for the base year (FY 2018) |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 emission reduction rate (compared to fiscal 2018) | 15.0% or more | 30.0% or more | 16.9% | 380,118t-CO2 | Organizational boundary (Scope of application): The financial control approach is adopted. Sales companies and offices, as well as production sites with CO2 emissions of less than 1,000 t-CO2, are excluded. Proportion of emissions covered by the reduction target: 100% |
| Water consumption reduction rate (compared to fiscal 2018) | 15.0% or more | --- | 14.8% | 5,229,801m3 | |
| Percentage of environmentally considered products in total sales of all products | 45.0% or more | --- | 36.7% | 31.9% | |
| Ratio of recycled lead used as lead raw materials in lead-acid batteries | 70.0% or more | --- | 72.4% | 36.8% | Ratio of utilization of recycled materials in main products |
Scope: Nine domestic business sites, 14 overseas business companies
Environmental Management
Operation of environmental management systems
At GS Yuasa Group, we are developing and using environmental management systems that comply with the ISO 14001 international standard.
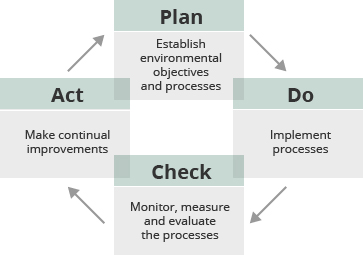
At every site, we use a PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act) cycle as part of a systematic framework for environmental management, enabling us to make continual improvements for environmental conservation.
PDCA Cycle
Organizational Structure
In the organizational structure for GS Yuasa Group's environmental management systems, the president of GS Yuasa serves as the chief executive officer responsible for environmental management, overseeing the environmental management of the entire Group working with officers in charge of environment under direct supervision. Environmental issues that affect the entire Group, such as fundamental environmental policy, are discussed and finalized at corporate executive management meetings.
We are also establishing environmental management systems for domestic business sites and overseas Group companies to enable quick and efficient communication within the group. Starting in fiscal 2018, we are expanding the scope of ISO 14001 certification, the international standard for environmental management systems, from our main domestic business sites to the entire Group, thereby building a system for strategically achieving the Group's environmental goals.
Overview of Organizational Structure

Acquisition rate of environmental management system certification at major production sites in Japan and overseas
| ISO 14001 certification | 82% |
| Environmental management system standards other than ISO 14001 | 18% |
| Total | 100% |
Environmental Auditing
We conduct internal environmental audits at every GS Yuasa Group business site to determine whether our environmental policy is being implemented appropriately and that environmental objectives are being met. In addition, we evaluate the environmental management system to improve performance as well as to improve the system itself. We also have an environmental certification agency conduct external environmental audits to check the conformity and effects of our environmental management systems.
Internal environmental auditing
Internal environmental auditors — with qualifications gained from training both inside and outside the company — determine the condition of the following:
- Compliance with environmental laws and regulations, etc. (legal compliance audit)
- Maintenance and management of environmental management systems (system audit)
- Degree of achievement of environmental objectives (performance audit)
External environmental auditing
Audits of the status of maintenance and management for environmental management systems based on ISO 14001 standards and the functioning of PDCA cycles confirmed that every organization subject to audit adheres to ISO 14001 standards. We will continue working to improve these systems by evaluating environmental management from a third-party perspective and by using information on such items as areas needing improvement.
Environmental Education
The GS Yuasa Group employs different types of environmental education to maintain and improve environmental management systems. In addition, we regularly provide training to avoid exposure to environmental risk.
General Environmental Education
| Education for Employees | In every division, we provide education to all employees to build awareness of their role in achieving the environmental policy. |
|---|---|
| Education for new recruits | New recruits are made aware of the GS Yuasa Group's basic philosophy on environmental management. |
Specialized Environmental Education
| Training of internal environmental auditors | At every business location, we train internal environmental auditors and provide them with education to boost their skills to continually improve our environmental management systems. |
|---|---|
| Emergency response training | In every division, we regularly provide training on responses to potential emergencies to all employees working in operations that have significant potential impact on the environment. |
Environmental Compliance Management
The GS Yuasa Group regularly reviews the environmental laws and regulations that must be obeyed, and ensures, through monitoring, that operations are managed in a way that is legally compliant.
Further, business is conducted in compliance with environmental laws and regulations since we use hazardous substances, such as lead, in our products and we must obey the laws and regulations related to the operation of recycling systems for used products.
There was no litigation and there were no punitive fines or administrative fines for nonadherence to environmental laws or regulations in fiscal 2024.
Environmental Risk Management
The GS Yuasa Group develops environmental risk management with consideration to the different needs of our stakeholders. In every business location, we work to prevent environmental pollution (atmospheric pollution, water contamination, etc.) through operational management based on voluntary standards that are stricter than regulatory standards based on environmental laws, regional ordinances and agreements.
In operations that have significant potential impact on the environment, we implement both tangible and intangible measures to reduce the risk of pollution. The tangible measures include: increasing the visibility of operations, preventing spills and using equipment to remove noxious substances. Intangible measures include: equipment inspections, monitoring, measuring and enhancing of operational procedures.
We also hold emergency response training regularly to help mitigate damage in an emergency situation.
In fiscal 2024 there were no instances of emergencies directly related to environmental pollution at any of our business locations.
Appropriate Environmental Information Disclosure
The Group conducts environmental information disclosure in response to the CDP*1. The CDP requires companies to disclose information of environmental strategies based on the needs of institutional investors and customers. As we recognize that climate-related issues are one of the important management issues, we are working on climate-related information disclosure based on the TCFD*2 framework.
For the volume of greenhouse gas emissions (including energy consumption), we disclose information for which authenticity of data has been secured through third-party verification*3. We are also promoting disclosure of information on water security performance and countermeasures with regards to water risks.
In the future as well, we are committed to working on disclosure of appropriate environmental information in response to the needs of various stakeholders.
1This is a global-standard information disclosure platform for corporate initiatives to address environmental issues (climate change, water security etc.), with an established mechanism in which scores calculated based on corporate information disclosure are used for evaluation by investors and others.
2An organization established by the Financial Stability Board at the request of G20 for examining climate-related information disclosure and ways in which financial institutions can respond
3We have received third-party verification from SGS Japan Inc. (Scope 2 verification data: CO2 emissions calculated based on the market-based method)
Statement on third-party verification (FY 2024)Refer here for information on our initiatives for the TCFD
Energy Management and Responses to Climate Change
Responses to Climate Change
The GS Yuasa Group maintains an awareness of the impacts of climate change on its business activities and on society and is proactively responding to these challenges. We promote initiatives for mitigating and adapting to climate change as well as sustainable technological innovation, and have formulated a strategy considering the risks associated with the transition to a decarbonized society as well as the risk of physical damage accompanying increased severity of natural disasters and extreme weather events. Specifically, we are enhancing our delivery of products that contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by improving our energy efficiency and promoting the utilization of renewable energy sources. We are also enhancing our disaster preparedness measures to respond to the impacts of natural disasters and extreme weather events while promoting the delivery of products and services to enable the maintenance of energy supply even in the event of a disaster. We are furthermore building a flexible and sustainable business model to accommodate the tightening of regulations and market changes, thereby ensuring business stability.
The Group will enhance its cooperation with stakeholders, including working closely with its supply chain, to actively contribute to the realization of a sustainable society through various climate change measures.
Reduction of CO2 Emissions by Promoting Group-wide Energy Management
The GS Yuasa Group believes that it is important to continuously improve the energy management system associated with its business activities and promotes the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in order to respond to the social changes accompanying the transition to a decarbonized society (such as requests from stakeholders to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, addition of carbon prices to the use of fossil fuels, and shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy).
To that end, the Group is working on formulating specific action plans under a specialized organization dedicated to promoting group-wide energy management, including promoting energy-saving measures in each business division and installing solar power generation systems at Group factories, in order to achieve our Carbon Neutrality Declaration targeting fiscal 2050 and our long-term environmental goals (reducing CO2 emissions by at least 30% by fiscal 2030 compared to fiscal 2018*). We also undertake continuous procurement of renewable energy from the market to facilitate the decarbonization of the electricity used in our in-house production processes.
The Group will continuously promote the effective use of energy in its business activities and actively engage in investment toward the mitigation of climate change. Specifically, we will optimize energy consumption in operational processes, introduce equipment and technologies that utilize less energy and which are highly effective, and enhance the utilization of renewable energy. We will promote process improvements and facilities investment aimed at furthering energy saving, particularly in production processes which consume large amounts of energy. In addition, for decision-making on facilities investment, we will carry out assessments that consider the in-house costs associated with greenhouse gas emissions (internal carbon price) and promote the introduction of high-efficiency equipment, the utilization of energy-saving technologies, and the installation of solar power generation systems. Through these initiatives, we will promote the transition to low-carbon business processes and assets, thereby actively aiming to achieve our carbon neutrality targets.
The Group manages CO2 emissions in totality and not on a basis of intensity, with the aim of reducing greenhouse gas emissions consistent with the Paris Agreement.
Main Measures Relating to Energy Saving and Renewable Energy (Fiscal 2024)
Please scroll sideways
| Classification | Items | Main Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Promoting measures to save energy | Review of facility renewal standards | Formulate an effective facility renewal plan (utilization of facility management ledger) |
| Improvement of production processes | ●Improvement of storage battery charging process, ●Examining for improvement of charging facilities | |
| Efficient use of production facilities | Thorough periodic inspections of capacity utilization status | |
| Introduction of solar power generation system in our own factories | Implementation of and examining for the plan to introduce solar power generation system | Investigation of the introduction of solar power generation system at business sites and Group companies in Japan |
| Procuring renewable energy | Procuring electricity derived from renewable energy | Use of electricity derived from renewable energy at the Kyoto Plant |
| Procuring renewable energy certificates | Procuring renewable energy certificates at overseas sites |
Usage Status of Renewable Energy at Our Factories (Fiscal 2024)
Please scroll sideways
| Country | Classification | Electric power (MWh) |
Reduction effects (t-CO2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | In-house power generation | 5,296 | 2,222 |
| External procurement | 53,856 | 22,566 | |
| United States | In-house power generation | 278 | 98 |
| United Kingdom | External procurement | 1,510 | 294 |
| Thailand | In-house power generation | 6,706 | 3,226 |
| External procurement | 35,000 | 16,835 | |
| Vietnam | In-house power generation | 154 | 78 |
| External procurement | 30,000 | 15,240 | |
| Indonesia | In-house power generation | 90 | 71 |
The renewable energy utilization rate for electricity used at our factories is 19.6%.
TOPICS
Introducing a Solar Power Generation system
The GS Yuasa Group is actively promoting the utilization of renewable energy to achieve our Carbon Neutrality Declaration and long-term environmental goals. A solar power generation system was installed at the Ritto Plant with total generating capacity of 4.2 MW in fiscal 2022 and fiscal 2023. In fiscal 2024, this system generated approximately 4,900 MWh of electricity, achieving CO2 emission reduction effects of approximately 2,000 tons. We will continue to install solar power generation systems utilizing renewable energy at other plants going forward.

Solar power generation system

TOPICS
Energy Conservation in Manufacturing Processes
Yuasa Battery (Thailand) Pub. Co., Ltd. is implementing energy-saving initiatives in manufacturing processes. In fiscal 2024, the company improved the combustion efficiency of burners installed in casting machines. Previously, incomplete combustion occurred due to improperly designed air intake ports during combustion, resulting in excess consumption of liquefied petroleum gas. To address this, the company added optimized air intake ports for some burners and made equipment improvements to achieve complete combustion. As result of this initiative, liquefied petroleum gas consumption was reduced by 49 tons in fiscal 2024, achieving a 147-ton CO2 emission reduction effect. The Group will continue to promote the efficient use of energy in order to curtail greenhouse gas emissions.

Casting machine
TOPICS
Making Energy-Related Information Visible Using a Portal Site
The Group established a dedicated portal site for promoting in-house energy conservation and disseminates related information. The portal site introduces specific case studies of initiatives for reducing energy and water consumption at business sites and in business divisions and also enables visualization of energy usage and provides energy-saving calculation apps. Through this initiative, we have increased employee awareness of energy-saving while enabling rapid and easy sharing of information on the challenges faced by business sites and divisions along with their solutions, leading to the planning and implementation of highly-effective energy-saving measures. The site also distributes information regarding the loan of energy-related measuring instruments, creating an environment where everyone can easily engage in “visualizing” energy usage. Going forward, we will actively use this portal site and make company-wide efforts to promote energy-saving measures.
Collaboration with Economic Organizations on the Mitigation of Climate Change
The GS Yuasa Group participates in the GX League*, which undertakes initiatives to transform the entire economic and societal system toward the aim of realizing a decarbonized society. The GX League is a platform spearheaded by the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI), for companies to collaborate with the government and academia in promoting the realization of carbon neutrality and societal transformation. Participating companies and organizations work together to enhance their competitiveness by means including the creation of new business opportunities and green markets for the transition to a decarbonized society. Through participating in the GX League, the Group is aiming to enhance its greenhouse gas emissions reduction strategy to achieve its carbon neutrality target. The Group also endorses the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations and indicates its business strategy toward the mitigation of climate change through an international framework to promote corporate financial disclosure on climate-related risks and opportunities.
The GS Yuasa Group will continue to cooperate with a diverse range of stakeholders, including economic organizations, and support the enhancement of policies to further expedite the transition to a decarbonized society.
GX, which stands for green transformation, refers to the transformation of the entire socioeconomic system through measures to create a decarbonized society.
Energy conservation activities for logistics
The GS Yuasa Group promotes energy conservation for freight forwarding (shipping) as one way to reduce the environmental burden during the product life cycle.
As part of coordinated efforts to save energy, we created a system to identify the quantity of goods being shipped, as well as energy consumption and CO2 emissions during logistics. We have established a system to identify the quantity of goods being shipped, as well as energy consumption and CO2 emissions during logistics, and are implementing energy saving measures such as reducing the quantity of items shipped between sites by integration of physical distribution bases and a modal shift from trucks to rail containers and other related systems for transportation.
In addition, the Group has been designated as certified by the Eco Rail Mark System* for three series of batteries for automobiles and motorcycles. By getting customers to purchase certified products, we are promoting activities in which customers and companies can participate together to reduce the burden on the environment.
Our Group promotes logistics that consider the environment by active utilization of rail freight transportation.
A system of certification by the Railway Freight Association, for companies and products that make thorough use of rail transportation for minimal environmental burden.

Examples of GS Yuasa Group products with Eco Rail certification
Water Security
Initiatives for Water Security
The Group uses a large amount of quality fresh water for applications such as dilution of electrolytes, which are storage battery materials, and cooling of storage batteries in the charging process. Since water resources are important natural resources for the continuation of business activities, we believe it is important to work on ensuring quality freshwater and reducing water consumption. Accordingly, the Group assesses water risks (flooding, drought, water stress, etc.) at production sites using the water risk assessment tools released by the World Resources Institution (WRI) as well as climate-related scenarios and the results of the Company’s own environmental impact assessments. In particular, the water intake volume at production sites determined to have high levels of water stress (three sites located in China, Turkey, and Thailand) is 737,327m³, accounting for approximately 17% of total water intake at all production sites. To effectively use limited water resources, including responses to water stress, the Group included targets for reducing water intake in production activities in all countries (15% reduction by fiscal 2025 compared to fiscal 2018) in its Mid-Term Management Plan and is implementing initiatives that are integrated with business strategies. We also respond appropriately to restrictions on water intake imposed by national and local governments.
In addition, in the production process of lead-acid batteries, water containing harmful substances (such as lead) is discharged. The Group recognizes the importance of properly treating wastewater so that such wastewater does not adversely affect the surroundings of our business sites. For this, we are committed to implementing wastewater management based on voluntary management standards that are stricter than regulatory standards, in order to ensure compliance with wastewater standards based on laws and regulations and regional agreements.
By securing water necessary for business activities and through an appropriate response to water risks such as environmental pollution around business sites due to wastewater, the Group aims to promote water security initiatives as well as realize the sustainable use of water resources. Further, we are responding to climate change-related risks based on the TCFD recommendations with respect to risks of damage due to floods (such as the shutdown of our factories due to flooding and disruptions in the supply chain).
Examples of a water risk initiative
Please scroll sideways
| Classification | Items | Main Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Water consumption | Reduction of water consumption | Reduction of wasteful use of water by improving manufacturing processes and implementing other measures, introduction of water-saving equipment, recycling of water used in production processes, and education of employees about saving water |
| Treatment of wastewater | Wastewater management | Thorough implementation and management based on voluntary management standards that are stricter than regulatory standards; regular maintenance and management of wastewater treatment facilities |
| Preventing under seepage | Installation of dikes at wastewater treatment facilities and impermeability of floor surfaces | |
| Responding to emergency situations | Establishing response procedures and training for emergency situations in case of water leakage |
Reduction of Water Consumption Associated with Production Activities
The Group promotes the effective use of water by taking measures at production plants such as recycling water and reducing water use.
At lead-acid battery plants, we are undertaking measures to reduce water intake including reusing cooling water, which is used in large volumes during the charging process, and recycling water that has been appropriately treated, such as rainwater and backwash water from industrial water filtration equipment. In addition, by switching the water nozzles of water-cooling devices in the outdoor units of dehumidifiers to spray nozzles at specialized battery factories, we are working to reduce the amount of cooling water used by air conditioning equipment while maintaining the necessary cooling performance.
Development and Provision of Environmentally Considered Products
Designing environmentally conscious products
The GS Yuasa Group's products have some impact on the environment during every stage of the product life cycle, from procurement and manufacturing to transportation, use and disposal. In order to reduce the environmental burden throughout the product life-cycle caused by the consumption of resources and the generation of greenhouse gases and waste, the Group is committed to improving the product performance through designing that considers selection of raw materials, ease of disassembly and segregation, energy conservation, and appropriate labelling.
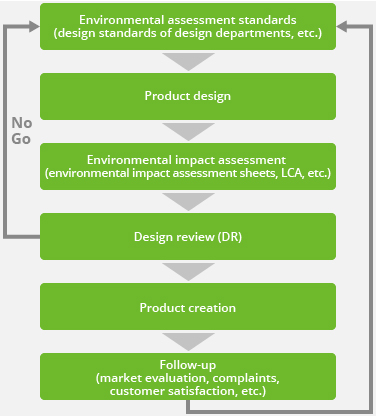
For an environmental assessment of product design, design departments employ design standards and then evaluate the suitability of products in design review (DR) meetings based on environmental impact assessments of every stage of the product life cycle. When environmental impact standards are not met, we review the design standards and redesign the product. We use the expertise of several departments in addition to design departments, including engineering, marketing, procurement, quality and the environment, to make sure that the results of Design for the Environment (DfE) are communicated widely, which also maximizes their effectiveness.
Environmental Assessment Items
- Energy conservation
- Volume reduction
- Recyclability
- Ease of disassembly
- Ease of separation processing
- Safety and environmental conservation
- Material selection
- Ease of maintenance
- Energy efficiency
- Reusability (life extension)
Flow of Environmental Assessment
Reflecting information in the products we distribute
Important information, such as customer requirements for GS Yuasa Group products, is used when we change the design of existing products or design new products. This helps boost the value of our Design for the Environment. Information from interested parties related to after-sales service, returns and complaints are used as a valuable resource to improve the environmental performance of products.
Management of chemical substances contained in products
The GS Yuasa Group takes steps to provide products with minimal environmental burden based on the Chemical Substance Management Guidelines, which clarify the standards for chemical substances in products. These guidelines are part of initiatives to examine chemical substances contained in materials delivered as stipulated in the GS Yuasa Group green procurement criteria. With these guidelines, we classify chemicals contained in our main materials, as well as the secondary materials and the parts used in the products that the Group makes and sells as either prohibited substances or managed substances. The GS Yuasa Group works with our suppliers who supply main materials, auxiliary materials and components to identify and definitively manage the substances covered by the guidelines to raise the environmental quality of our products.
Popularizing environmentally considered products
The GS Yuasa Group defines environmentally considered products as those products that help mitigate global warming, and we are actively working to develop and popularize such products. We incorporate into the Group's Mid-Term Management Plan sales targets for environmentally considered products, making it part of our business strategy to work on climate change through the products we provide to customers.
Examples of Environmentally Considered Products
| Item | Description | Examples of products |
|---|---|---|
| Batteries for vehicles with start-stop systems | Batteries for vehicles with start-stop systems (ISS) for improving gas mileage by allowing the engine to stop instead of idling to reduce fuel consumption | |
| Storage battery system | A system to effectively utilize renewable energy (power conditioners, lithium-ion battery, etc.) | |
| Automotive Lithium-ion Batteries | Hybrid vehicle batteries and electric vehicle batteries that contribute significantly to reducing greenhouse gases |
Click image to enlarge
Increasing Usage Rate of Recycled Lead in Products
The GS Yuasa Group is working to increase the usage rate of recycled lead—the primary material used in lead-acid batteries, one of our core products. We take action to work toward a recycling-oriented society as part of our business strategy by incorporating into the Group's Mid-Term Management Plan targets for the usage rate of recycled lead contained in our lead-acid batteries.
The GS Yuasa Group has been taking action to recycle our post-use products by building and operating a recycling system based on extended producer responsibility (EPR). Going forward, we also plan to strengthen our efforts to promote the use of recycled materials in our products.
Refer here for data on changes in the ratio of recycled lead used as raw material in lead-acid batteriesContribution to Creating a Recycling-Oriented Society
Waste Management
The Group considers that promoting effective utilization of resources as well as the 3Rs (reduce: reduce waste generation; reuse; and recycle) are crucial for contributing to the realization of a recycling-oriented society. As lead-acid batteries that constitute the Group's main product use harmful substances (such as lead) as raw materials, we recognize the importance of proper disposal of waste generated in our production processes.
By promoting quality improvement activities aimed at reducing in-process defects, the Group ensures reduced waste generation (including hazardous waste). In addition, we are committed to reducing the amount of waste generated by reusing raw material loss (such as lead scrap) in the production processes. As for recycling, we are engaged in activities to improve the rate of recycling of resources. We have also established a system to ensure proper disposal of waste in accordance with laws and regulations so as to prevent improper waste disposal (including illegal dumping).
Examples of initiatives for effective use of resources
- Strict implementation of waste separation rules
- Appropriate selection of recycling companies
- Reusing raw materials loss
Examples of operations to ensure proper waste disposal
- Establishing a company-internal system to promote proper waste management
- Strict implementation of waste separation and waste storage rules
- Periodic on-site inspections of waste disposal contractors
- Nurturing personnel in charge of waste disposal practices (including implementation of regular education on waste)
Refer here for data on waste-related changes (amount of recycling, quantity of final disposal)
TOPICS
Reducing Sludge Discharge
At the Kyoto Plant, we are working to reduce the large volumes of wastewater treatment sludge that is discharged within the plant site. In fiscal 2023, we took action to reduce the amount of water contained in sludge. Previously, sludge was manually dewatered, but new sludge dewatering equipment (a belt press dewatering machine) and dewatered sludge dryer were installed. We built the dryer ourselves to operate on solar power and reduce environmental impact. As a result of these changes to sludge dewatering and drying work, the amount of sludge was reduced by 4,570 kg (approximately 3%) from the previous year, work efficiency was increased, and work safety is insured. The water that is released during the dewatering process is properly treated in a wastewater treatment plant.

Belt press dewatering machine

Dewatered sludge dryer
TOPICS
Reuse of Wooden Pallets
At the Gunma Plant, we are taking measures to process and reuse wooden pallets that were used for products delivered from overseas. Through these measures, we are reducing the number of new wooden pallets procured and achieving effective utilization of resources. In fiscal 2024, approximately 25% of the wooden pallets used at the Gunma Plant were reused, leading to a reduction in new procurement. To contribute to the realization of a circular economy, the Group will continue working on waste reduction in effective resource utilization.

Processed wooden pallets
TOPICS
Environmentally Considered Road Paving
At our Gunma Plant, we have repaved the roads on the premises using asphalt modifiers generated from collected waste plastic bottles. In fiscal 2024, these modifiers were used on approximately 8,800m2 of road surfaces, improving the durability of the asphalt pavement while achieving the effective use of resources. The GS Yuasa Group also promotes initiatives that take environmental impact into consideration for infrastructure improvements on our plant premises.

Environmentally considered road pavement on the premises (Gunma Plant)

Recycling Plastic Resources
Since the GS Yuasa Group uses plastics for such things as product materials and packing materials, we recognize the importance of promoting initiatives for the streamlining of plastic resources, which do not easily decompose in the environment, and reducing and recycling waste plastics. The GS Yuasa Group, in the operational management of our environmental management system based on ISO 14001 certification, identifies the use and disposal of plastics as key environmental issues and promotes initiatives for recycling plastic resources.
Examples of initiatives for recycling plastic resources
Efficient use of plastic resources and utilization of alternative materials
- Reducing waste from resin parts through measures to reduce in-process defects
- Reducing the usage of product packing materials through employing high-elasticity stretch film
- Achieving long-term usage of cushioning materials used for storing semi-finished products through employing highly durable Styrofoam
- Manufacture of products using recycled resins
- Adoption of long-life pipe materials
- Raising awareness in design departments to achieve long-life products
Reusing plastic materials
- Reusing plastic scraps generated in the production process for product materials
- Reusing plastic materials used in the production process (storage bags, PP band, stretch film, air packs, foam materials, resin pallets)
- Reusing resin pallets and plastic office supplies
Recycling waste plastic
- Purchasing recyclable office supplies and simple packing supplies (printer ink, label printer cartridges, etc.)
- Thoroughly separating waste plastics (packing materials, PP band, office supplies, food packaging materials, etc.)
- Promoting material recycling for waste plastics (Eco Cap, Styrofoam, etc.)
- Utilizing thermal recycling for waste plastics
Resource Recycling of Used Product
The GS Yuasa Group believes in the importance of creating and operating a system for recycling resources from our used products to help create a recycling-oriented society. To achieve this goal, the Group is promoting initiatives for processing used products and resource recycling by using the wide area certification system.
A wide-area certification system aims to involve the manufacturers of a product in the product's recycling and disposal once it reaches the end of its useful life. These systems make possible more efficient recycling and provide feedback on product design leading to easier disposal and reuse, while ensuring that discarded goods are disposed of properly.
In January 2008, the GS Yuasa Group in Japan acquired wide-area certification from the Ministry of the Environment for industrial batteries and power supplies, and in January 2009 started accepting orders in earnest for a recycling system based on this certification. Even following the start of operations, we continue to make improvements such as expanding the scope of covered products and reviewing operational rules to create mechanisms for the reliable and proper disposal of used industrial batteries.
In the future, we will promote even more effective operation of the wide-area certification system to improve customer service as well as to recycle and properly dispose of post-use products.
Chemical Substance Emissions Management
Identifying chemical substance emissions
Today, chemical substances used at GS Yuasa group's business sites include those subjects to reporting under the PRTR Law*. The Group incorporates the management of hazardous substances into environmental management and regularly assesses how they have been handled to reduce environmental risk and related legal compliance.
PRTR (Pollutant Release and Transfer Register) Law
This law covers identifying, etc., the emissions of specific chemical substances into the environment and promotes improved management. The law requires businesses to collect, tabulate and disclose data related to hazardous chemical substances, their sources, the amount of emissions and how much is transferred out of the plant, including as waste.
Class I Designated Chemical Substances (substances that may damage people's health or interfere with the growth of animals and plants) are subject to reporting under the PRTR system. Of these substances, those that have carcinogenic properties are classified as Specific Class I Designated Chemical Substances.
Preventing Atmospheric Pollution
The Group believes that to prevent any damage to the health and the living environment of local residents, it is crucial to appropriately process substances that are emitted into the atmosphere in the course of our business activities. For this, we are committed to thorough implementation of our environmental management system that conforms to international standards and which ensures that our operations are in compliance with atmospheric emission standards based on laws and regulations concerning soot and smoke, dust, volatile organic compounds, etc. as well as regional agreements. Also, by adopting appropriate measures to prevent atmospheric pollution (installation of dust collectors and maintenance and management of related equipment, etc.), we are making efforts to prevent adverse effects of atmospheric pollution in the vicinity of our business sites. Further, we regularly monitor, and adopt appropriate measures in response to, updated information on atmospheric pollution standards of national and local governments.
Biodiversity Conservation
Identifying Dependencies and Impacts on Nature of Business Activities
The Group recognizes that while we receive many benefits from ecosystems at each stage from procurement of raw materials, such as lead, to production, distribution, and disposal of products, we also impose certain burdens on ecosystems. Therefore, we view biodiversity conservation as a necessary initiative for sustainable business operations.
Based on this awareness, we begin a systematic analysis of the relationship between our business activities and nature in fiscal 2024 to understand and appropriately address the Group's dependencies and impacts on nature.
To perform this analysis, we first organized our business activities across the value chain and then comprehensively considered information on dependencies and impacts on nature obtained from ENCORE* along with the actual conditions of the Group. In fiscal 2024, we selected the automotive lead-acid batteries business, which accounts for more than half of our sales. Considering information availability and other factors, we also focused on the domestic automotive lead-acid battery business. Next, based on distance from key biodiversity areas (KBA) and water risk assessment results, we identified priority business sites from among domestic business locations and identified the elements on which those sites depend on nature and the impact they have on nature based on ENCORE* information and the conditions at each site.
In the future, we will investigate specific measures based on the analysis results, expand the scope of analysis, and continuously reinforce measures for biodiversity conservation throughout the Group.
ENCORE (Exploring Natural Capital Opportunities, Risks and Exposure) is a tool for analyzing and evaluating how business interacts with nature. The degree of dependency and impact is evaluated on a five-level scale (very high, high, medium, low, and very low).
Business Activities in the Group’s Value Chain
| Value chain | Process | Business activities |
|---|---|---|
| Direct operations | Production | Manufacture of automotive lead-acid batteries, automotive lithium-ion batteries, industrial batteries, specialized batteries, and power supplies |
| Sales | Sale of automotive lead-acid batteries, automotive lithium-ion batteries, industrial batteries, specialized batteries, and power supplies | |
| Upstream | Procurement & distribution | Extraction of lead and lithium, lead refining |
| Manufacture of sulfuric acid and plastic raw materials, etc. | ||
| Transport of raw materials | ||
| Downstream | Assembly of final products | Manufacture of automobiles and electrical equipment |
| Disposal & recycling | Recycling of end-of-life lead-acid batteries (lead refining, plastic recycling) and end-of-life lithium-ion batteries |
Dependencies and Impacts on Nature in the Domestic Automotive Lead-Acid Battery Business
Please scroll sideways
| Value chain | Business activities | Number of sites that should be prioritized | Dependencies | Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct operations | Manufacture of lead-acid batteries | 2 | Use of large volumes of fresh water in the charging and plate manufacturing processes for storage batteries | ●Soil contamination and water pollution from the release of wastewater that contains lead and other heavy metals ●Depletion of water resources from the use of large volumes of water in the manufacturing process of storage batteries |
| Upstream, downstream | Lead refining | 2 | Use of large amounts of fresh water for cleaning to prevent dust from scattering during the lead refining process and for wastewater treatment | ●Release into the atmosphere of substances and soot, such as SOx, Nox, and lead, generated during combustion ●Negative impacts on the surrounding natural environment from noise and vibration caused by operation of machinery ●Soil contamination and water pollution from the release of wastewater that contains lead and other heavy metals |
TOPICS
Initiatives for Biodiversity
■Kyoto Plant
At our Kyoto Plant, we have participated since fiscal 2021 in the Futaba Aoi Cultivation Program organized by the Afuhi Project located in the premises of the Kamigamo Shrine in Kyoto City, and are involved in the cultivation of the Futaba Aoi, a plant endemic to Japan, in the plant premises. In addition, the cultivated Futaba Aoi plant was handed back to Kamigamo Shrine in May 2025, and this returned Futaba Aoi will be used for the Aoi Katsura at the Aoi Festival, one of the three major festivals in Kyoto. From next year as well, we plan to our participation in the Afuhi Cultivation Program and are committed to considering and promoting appropriate biodiversity initiatives to which the Group can contribute.
Afuhi Cultivation Program: The cultivation of Futaba Aoi by "Aoi no Mori" located in Kamigamo Shrine is a program to cultivate the Futaba Aoi externally (that is by individuals, companies etc.). This is because there is a high risk of animal damage attributed to deer and moles and abnormal weather, etc. A project that aims for external cultivation of Futaba Aoi (by individuals, companies etc.) to avoid the high risk of animal damage attributed to deer and moles and abnormal weather when the Futaba Aoi is cultivated in the "Aoi no Mori" situated within the premises of the Kamigamo Shrine.

Futaba Aoi

Offering the Futaba Aoi
■GS Yuasa Siam Industry Ltd.
To protect the local ecosystem, GS Yuasa Siam Industry Ltd. (GYSI), an overseas Group company in Thailand, has planted and grows wild almond trees (a native species known locally as the samrong tree/สำโรง) around its factory in an effort to prevent the growth of alien species. This initiative has won high praise from Chachoengsao Province, where GYSI is located, and in fiscal 2023 the company received the Good Governance Environment Promotion Award presented to companies operating in the province that are making efforts toward the realization of a sustainable industry and society.

Trees planted at the factory site

Recent photo of wild almond tree blossoms

GYSI received the Good Governance Environment Promotion Award
■GS Yuasa Battery Manufacturing UK Limited
GS Yuasa Battery Manufacturing UK Limited (GYMUK), an overseas Group company in the United Kingdom, established a biotope of about 400 m2, with a pond and grassland, in the factory grounds, creating an ecosystem inhabited by various creatures, including birds, fish, and insects. This biotope secured the top place in the Blaenau Gwent in Bloom award from 1988 to 2020, presented to beautiful gardens by the county of Gwent in Wales, where GYMUK operates.

Biotope scenery (stone monument)

Biotope scenery (pond)

Blaenau Gwent in Bloom awards










